Talking about cable production process: stranding of conductors
Stranding (stranded wire): The process of twisting multiple monofilaments with smaller diameters into larger cross-section conductive cores according to certain rules.
1. There are two types of twisted wires: regular twisting and irregular twisting.
Regular stranding can be divided into regular concentric single-wire stranding and regular concentric strand stranding. Regular concentric single-wire stranding:
⑴ Ordinary stranded wire: Use a single wire of the same diameter to twist regularly one layer after another in a concentric circle, and the twisting direction of each layer is opposite.
⑵ Combination stranded wire: it is stranded by single wires of the same diameter, different materials, or different diameters and different materials. (Representative products such as overhead wires)
Regular concentric strand stranding: It is a stranded wire that is concentrically stranded by multiple ordinary stranded wires or bundles.
Irregular twisting (beam wire): A twisted wire formed by multiple single wires twisted together in the same twisting direction and not according to the twisting law. The position of each single wire is not fixed to each other, and the shape of the bundle wire is also difficult to maintain a round shape. whole.
2. The biggest difference between bundled wire and ordinary stranded wire is: each monofilament of ordinary stranded wire has a fixed position, which is regularly twisted layer by layer; there is no fixed position between the monofilaments of the bundled wire It is twisted together without following the twisting rule.
3. The characteristics of irregular twisting (beam line): Since each single wire in the beam line is twisted in one direction, the sliding margin between the single wires is large when bending, and the bending resistance is small, so the bending performance of the beam line Particularly good, for wire and cable products that require flexibility and frequent movement of the term, the bundle wire is used as the conductive core.
4. Features of stranded core:
⑴ Good flexibility; the use of multiple smaller diameter monofilament twisted cores can improve the bending ability of the cable, and facilitate the processing, manufacturing, installation and laying of wires and cables.
⑵ Good stability; multiple monofilaments are twisted into a core according to a certain direction and twisting rules, because the position of each monofilament in the strand is in the elongation area of the upper part of the strand and the lower part of the strand in turn. In the compression zone, no deformation occurs when the twisted wire is bent.
⑶ Reliability is good; single wire is used as conductor of wire and cable, it is easy to be affected by material inhomogeneity or defects in stranding, which will affect the reliability of conductive core. Defects such as cores made of multiple single wires can be obtained. In order to disperse and not concentrate on a certain point of the conductor, the reliability of the conductive core is much stronger.
⑷ High strength; compared with multiple stranded cores of a single wire of the same cross-section size, the strength of the stranded core is higher than that of a single wire.

5. Term explanation:
(1) Pitch: the distance of a single wire moving forward in the axial direction.
(2) Pitch diameter ratio: the ratio of the pitch length of the twisted wire to the diameter of the twisted wire.
(3) The relationship between the pitch and the softness of the twisted wire: the smaller the pitch, the better the softness of the twisted wire. On the contrary, the larger the pitch, the worse the softness of the twisted wire.
(4) Stranding factor: the ratio of the actual length of the unfolded monofilament to the pitch length in a pitch of the stranded wire.
(5) The twisting direction of the twisted wire: right (Z direction) and left (S direction)
(6) Compressed conductor: the common compressed conductors are compressed round, sector and compressed tile (five-core cable) semi-circular (two-core cable)
6. Purpose of pressing:
(1) Squeeze fan-shaped conductors: reduce the outer diameter of the cable, save product costs and reduce the weight of the cable.
(2) Compact circular conductor: Improve the surface quality of the stranded conductor, reduce the conductor diameter, and increase the conductor filling factor. The compacted conductor surface is smooth and round without burrs, and the electric field on the conductor surface is uniform. Save materials and reduce costs.
7. Conductor classification:
According to the GB/T3956 "Cable Conductor" standard, there are four types of conductors, namely the first, the second, the fifth and the sixth. The first type is a solid conductor, and the second type is a stranded conductor, both of which are suitable for the conductors of fixed laying cables; the fifth and sixth types are twisted conductors, which are used for the conductors of flexible cables and cords. The sixth type is better than The fifth is softer.


 Company Profiles
Company Profiles Company Culture
Company Culture Message
Message Honor
Honor Video Center
Video Center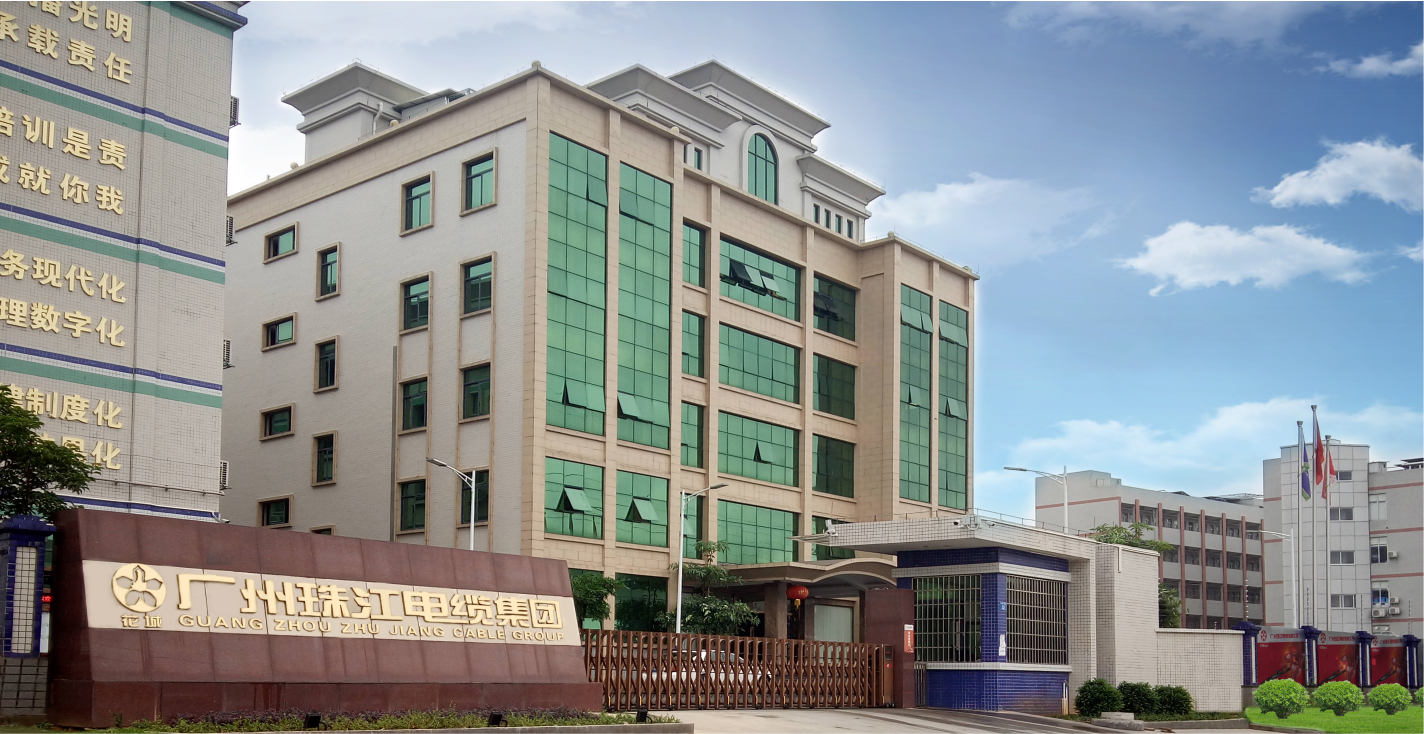 Company Reality
Company Reality Pearl River Cable
Pearl River Cable Low Voltage Cable
Low Voltage Cable Medium Voltage
Medium Voltage Mineral Cable
Mineral Cable Control Signal Cable
Control Signal Cable Corporate News
Corporate News Cable Information
Cable Information Media Reports
Media Reports Network Reprint
Network Reprint