National standard wire diameter table and calculation method
National standard wire diameter table and calculation method
National standard wire diameter table
Wire (square mm) | Conductor diameter (mm) |
1.5 | 1.38 |
2.5 | 1.78 |
4 | 2.25 |
6 | 2.76 |
10 | 1.33×7 |
16 | 1.70×7 |
25 | 2.10×7 |
35 | 2.50×7 |
50 | 1.78×19 |
70 | 2.10×19 |
95 | 2.50×19 |
Note: The above conductor diameter refers to BV plastic copper wire and BLV plastic aluminum wire
Conversion method: know the square of the wire, calculate the radius of the wire with the formula for calculating the area of the circle: wire square number (square millimeter) = pi (3.14) x wire radius (mm) square
Knowing the square of the wire, the same is true for calculating the wire diameter. For example, the wire diameter of a 2.5 square wire is: 2.5 ÷ 3.14 = 0.8, and the square root is 0.9 mm, so the wire diameter of a 2.5 square wire is: 2×0.9 mm = 1.8 Mm.
Knowing the diameter of the wire, the square of the wire is also calculated by the formula for finding the area of a circle: the square of the wire = the circumference of the circle (3.14) × the square of the wire diameter/4
The cable size is also nominally squared, and the multi-stranded wire is the sum of the cross-sectional area of each wire. The calculation formula of the cable cross-sectional area: 0.7854 × the square of the wire radius (mm) × the number of strands such as 48 strands (each wire with a radius of 0.2 mm) 1.5 square wire: 0.785 × (0.2 × 0.2) × 48 = 1.5 square


 Company Profiles
Company Profiles Company Culture
Company Culture Message
Message Honor
Honor Video Center
Video Center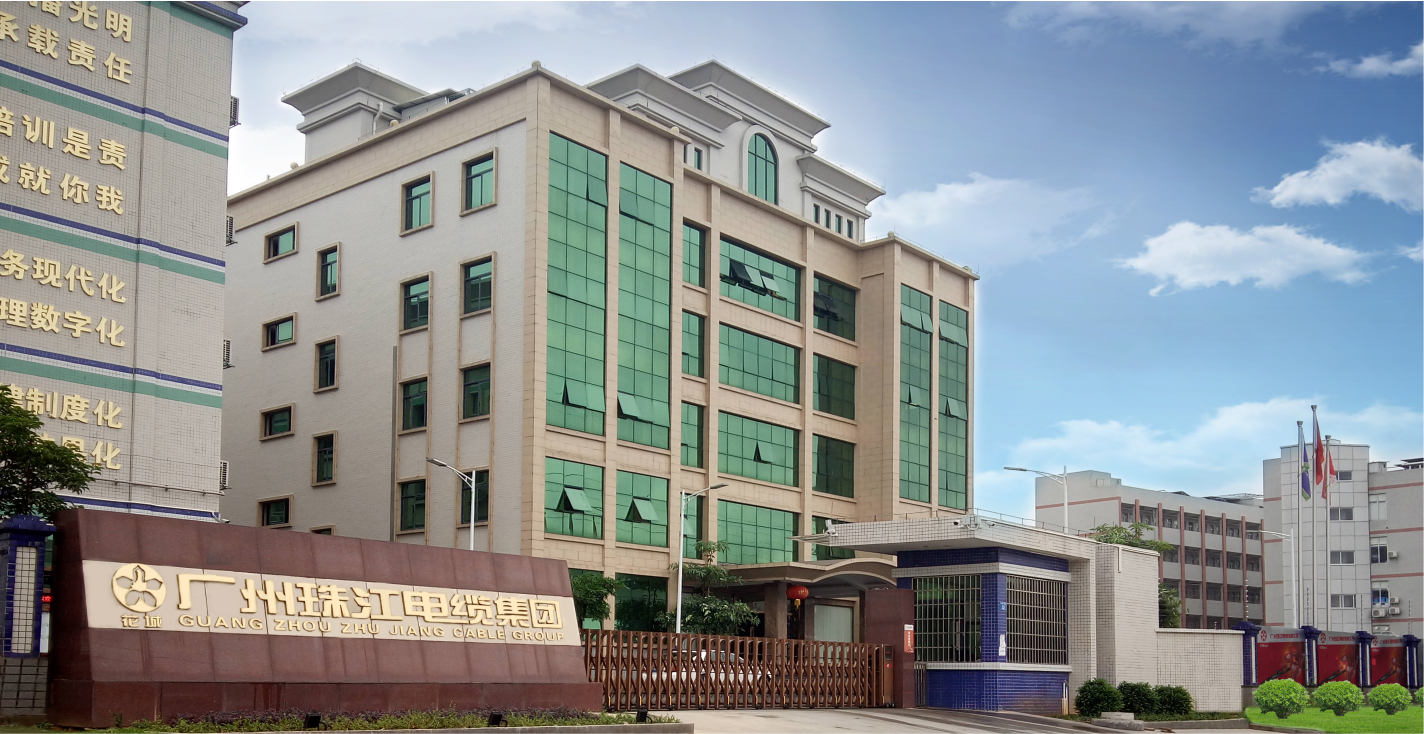 Company Reality
Company Reality Pearl River Cable
Pearl River Cable Low Voltage Cable
Low Voltage Cable Medium Voltage
Medium Voltage Mineral Cable
Mineral Cable Control Signal Cable
Control Signal Cable Corporate News
Corporate News Cable Information
Cable Information Media Reports
Media Reports Network Reprint
Network Reprint