Huacheng Cable|What is the relationship between the rated voltage of the cable and the number of cable cores, and how to choose?
Huacheng Cable|What is the relationship between the rated voltage of the cable and the number of cable cores, and how to choose?

1. Selection conditions for 1~5 core cables of 1kV and below
(1) Single core cable
To avoid or reduce intermediate joints when the circuit is longer, the working current is larger or the circuit is laid underwater, or the single-core cable has better comprehensive technology and economy than the multi-core cable, the single-core cable can be used.
Low-voltage DC power supply loop, single-core cable can be used when needed.
(2) Core cable
When the neutral point of the power supply of 1kV and below is directly grounded, the number of cores of the single-phase circuit cable. When the protection line and the neutral line share the same conductor, a 2-core cable should be used.
A 2-core cable should be used for the DC power supply loop.
(3) Core cable
When the neutral point of the power supply of 1kV and below is directly grounded, the number of cores of the single-phase circuit is: when the protection line and the neutral line are independent, a 3-core cable should be used.
(4) Core cable
For 4-core cables (3+1 cables) of 1kV and below, the 4th core in addition to being used as a protective ground, also transports unbalanced current and short-circuit current in the power system. Its size is determined by unbalanced current and short-circuit current, but generally it should not be less than 1/2 of the phase line.
For three-phase four-wire low-voltage power distribution systems of 1kV and below, when the protection line and the neutral line share the same conductor, a 4-core cable should be used instead of a 3-core cable plus a single-core cable to form a loop, or even directly Use the metal sheath or armor layer of the 3-core cable as the neutral wire. Otherwise, when the three-phase current is unbalanced, it is equivalent to the operating state of a single-core cable, which is likely to cause power frequency interference.
(5) Core cable
Three-phase four-wire low-voltage power distribution systems of 1kV and below, some electrical equipment distribution lines with high safety requirements, and some communication centers and automation equipment that need to ensure electrical safety and anti-interference grounding should be used The 5-core TN-C low-voltage power distribution system makes the protection line (PE line) and the neutral line (PN line) independent. The cross-sectional area of the cable core is generally 3 large 2 small or 4 large 1 small or 5 large.

Second, the choice of the number of cores in the medium and high voltage cables
For the selection of the number of cores of the 3~35kV three-phase power supply loop cable. When circuits with larger operating currents or cables are laid underwater, 3 single-core cables can be used for each circuit; in addition to the above cases, 3-core cables should be used, and 3-core cables can be used for general package type or 3 A single-core cable stranded structure type.
For the 110kV three-phase power supply circuit, 3 single-core cables can be used for each circuit, except for laying in lakes, under the sea and other places and the cable section is not large.
For three-phase power supply circuits above 110kV, 3 single-core cables should be used for each circuit.
For high-voltage AC single-phase power supply circuits such as electrified railways, 2-core cables or 2 single-core cables should be used each time.
Single-core cables should be used for HVDC transmission systems; coaxial 2-core cables can also be used when laying underwater in lakes, seas, etc.


 Company Profiles
Company Profiles Company Culture
Company Culture Message
Message Honor
Honor Video Center
Video Center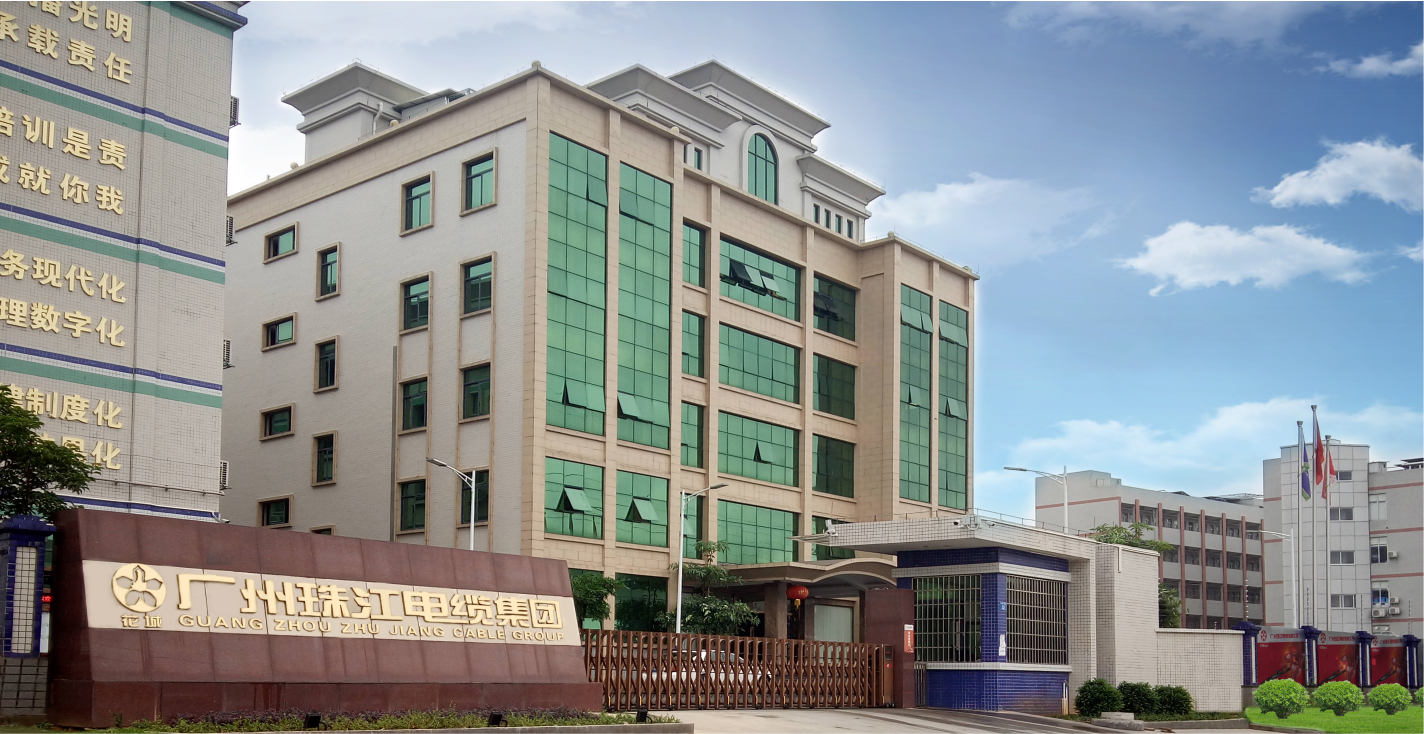 Company Reality
Company Reality Pearl River Cable
Pearl River Cable Low Voltage Cable
Low Voltage Cable Medium Voltage
Medium Voltage Mineral Cable
Mineral Cable Control Signal Cable
Control Signal Cable Corporate News
Corporate News Cable Information
Cable Information Media Reports
Media Reports Network Reprint
Network Reprint