What are the causes of overheating of wires and cables in use?
What are the causes of overheating of wires and cables in use?

When the wire and cable are energized, the metal core will heat up. As the energization time increases, the surface temperature of the wire and cable will become higher and higher. If it is not handled in time, the consequences can be imagined. Our commonly used PVC wire and cable, the sheath is polyvinyl chloride, taking the core temperature of 70 degrees as the upper limit, the surface temperature will be 5-10 degrees lower. Therefore, it is safe for the cable surface temperature to be below 60 degrees. From the perspective of power supply maintenance, of course, the lower the temperature, the better.
It is normal for wires and cables to heat up, but there are some conditions that can cause the wires and cables to overheat. Today, Zhujiang Cable's editor will talk about the reasons for the overheating of wires and cables in use.
1. Reasons for overheating of wires and cables in use
1. The wires and cables are not tightly crimped during the joints, resulting in excessive resistance at the joints, which may cause the wires and cables to overheat when they are energized for a long time;
2. In the design, planning and installation of wires and cables, they were not fully considered, and wires and cables that did not match the resistance of the cable conductor were selected. When the energizing current is greater than the large negative current, it will cause overheating;
3. Improper selection of the cable type causes the conductor cross-section of the cable used to be too small, and overload occurs during transportation. After a long time of use, the heating and heat dissipation of the cable will be unbalanced, resulting in overheating;
4. Due to the unprofessional installers, the cables are arranged too densely during installation, the ventilation and heat dissipation effect is not good, or the cables are too close to other heat sources, which affects the normal heat dissipation of the cables, and may also cause the cables to overheat during operation;
5. The insulation performance between phases of the cable is not good, resulting in low insulation resistance and overheating during transportation;
6. The partial sheath of the armored cable is damaged, causing slow damage to the insulation performance after the water enters, causing the insulation resistance to gradually decrease, and also causing overheating during the operation of the cable;
7. Many inferior wires and cables on the market have poor insulation properties, resulting in reduced insulation resistance and overheating after long-term operation;
8. Improper selection of wire and cable models, such as fire-resistant wires and cables in high temperature or flammable environments.


 Company Profiles
Company Profiles Company Culture
Company Culture Message
Message Honor
Honor Video Center
Video Center Company Reality
Company Reality Pearl River Cable
Pearl River Cable Low Voltage Cable
Low Voltage Cable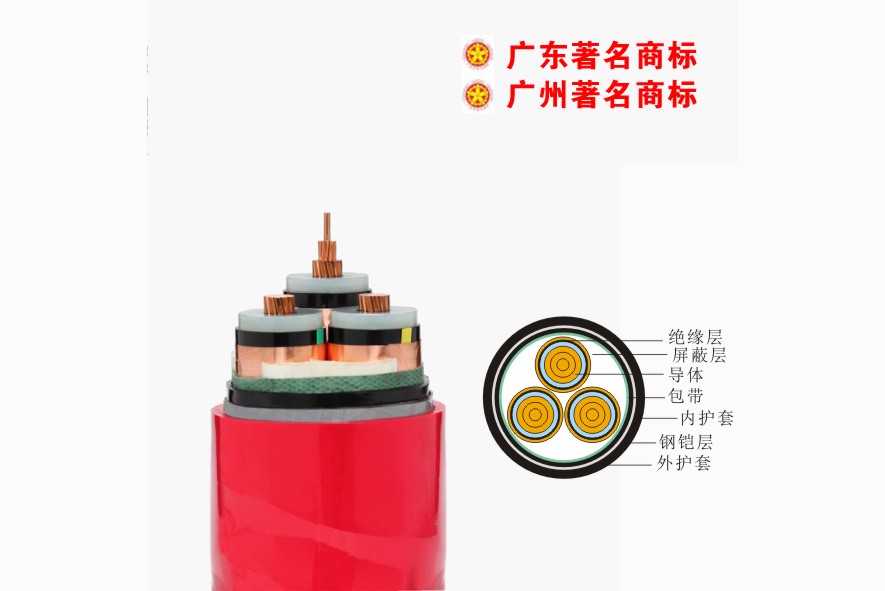 Medium Voltage
Medium Voltage Mineral Cable
Mineral Cable Control Signal Cable
Control Signal Cable Corporate News
Corporate News Cable Information
Cable Information Media Reports
Media Reports Network Reprint
Network Reprint