Several common problems in cable laying methods
Several common problems in cable laying methods

Directly buried
For direct burial laying, it is necessary to consider whether the cable is susceptible to damage caused by external impact.
1. If there is no big impact, it is possible to lay it directly.
2. If it is possible to receive some relatively large impacts, but the strength can be controlled within a certain range, you can consider armored direct burial.
3. If the external force is greater, it is necessary to use a protective sleeve, which can be set locally (such as a place through a highway).
Advantages and disadvantages of direct buried cable laying
Advantages: easy to lay, saving materials and labor,
Disadvantages: maintenance is inconvenient. If maintenance is required, the overburden needs to be excavated. It is only recommended to use in places where maintenance is not considered or can be accepted. Generally, yellow sand is required for direct burial.
Question 1. How to find the fault point for the direct buried cable grounding?
Answer: Use the patrol cable tester.
Question 2. Does the direct buried cable need to be a cable well?
Questions added: Cable laying in the factory area is directly buried with armored cables. Do you need to add cable wells at crossings and entering the power distribution room of the workshop? Is it necessary to add cable wells when municipal 10KV cables enter the factory?
Answer: Cable wells are not required for cables with 6 or less. There are many wells for cables, which is easy to replace and add cables. The municipal 10KV cable does not need to set up a cable well when it enters the factory area, it can be directly buried from the terminal pole to the high-voltage power distribution cabinet.
Question 3. How to lay temporary cables on the construction site?
Supplement to the problem: The unit builds a new factory building, and the transformer and high-voltage line are far away from the construction center. Because it is a steel structure factory building, overhead lines cannot be used to avoid conflicts with steel structure installation. Only low-voltage cables can be used to lead from the transformer to the construction site. Class-level distribution box, and then allocated to the second-level distribution box of each construction unit on site. How to lay this section of low-voltage cable? Is it buried directly or placed directly on the ground?
Answer: It is strictly forbidden to lay directly on the ground. This low-voltage cable is directly buried.
Pipe laying
Compared with direct burying, cable laying through pipes is more convenient for later maintenance and adding lines. For cables laid through pipes, some spare pipes can be considered to prepare for future line maintenance and capacity expansion.
1. When laying through pipes, it is necessary to consider setting up cable wells when the turning angle of the line is large or the distance of the straight section is long.
2. When the number of cables is small and the wire diameter is small, the cable hand well can be used;
3. In the case of more cables and larger wire diameters, it is necessary to consider setting up cable manholes. The cable well can be done in accordance with the atlas. In addition to the atlas approach, many small passage wells can also be directly built by brick or concrete. At this time, it is necessary to consider setting up water seepage holes at the bottom.
4. There are many pipes that wear pipes, such as cast iron pipes, steel pipes, polyethylene pipes, nylon pipes, carbon pipes, etc., which can be selected according to needs. Pay attention to the influence of eddy current when single-core cables pass through metal pipes.
Pipe laying
Pipe laying is mainly used in areas with more lines and concentrated routes. Relatively speaking, pipe laying is more convenient and saves materials.
Question 1. When laying cables in outdoor pipes, is it one row of pipes, one cable, or multiple cables can be used in one row?
Answer: Each tube should only wear 1 cable. Except for important places such as power plants and substations, for all circuits of a motor or all circuits of a low-voltage motor of the same equipment, no more than 3 power cables or multiple control cables can be combined in each tube. For details, see GB 50217-2007 P32 5.4.4.
Question 2. What should I do if the laying depth of the piping is not enough?
Question supplement: How to bury cable ducts on the ground less than 1m thick? Below is the basement. The ceiling of the basement is only 70 to 80 cm thick, and the well depth is 1.3 meters?
Answer: If in an area with no vehicles, the buried depth should not be less than 0.5m (the cable specification requires 0.5m, and the civil code requires 0.7m. Here, the cable specification shall prevail). If there are more vehicles passing, you can add a protective plate on the pipe. Or use thick-walled steel pipes for laying or use cable trenches. If the roof of the basement has only 70-80 cm of soil, the depth of the well should be 1.3m to lower the roof, but this is of little significance, because the drainage problem of the cable well is difficult to solve, and few people pay attention to it.
Question 3.Is there a problem with the laying of strong current pipes and weak current pipes?
Question supplement: There are a dozen low-voltage and high-voltage cables in the factory area, and there are also weak-current (TV, telephone, network) cables. There are more than 8 strong-current cables, and they can’t be buried directly. I used pipes. Laying. But now there is a problem, that is, the weak current is also laid through the pipe, so can the strong current tube and the weak current tube be arranged together?
Answer: Try not to line up together. When doing small municipal administration, try to install strong and weak electric pipes on both sides of the road. If there is occasional crossing, it is recommended to implement it in accordance with the specification spacing requirements. You can refer to the atlas, such as the laying of underground communication cables 05X101-2.
Question 4. Outdoor cable concrete pipe laying?
Question supplement: When drawing the general plan, all outdoor cables shall be laid with concrete pipes at the request of Party A. After consulting the atlas (94D164), the following problems were found:
1. Due to the influence of other pipelines on site, except for straight wells, the cable piping work manhole wells cannot be in accordance with the size shown in the atlas. I wonder if there is any reasonable solution?
2. Regarding the drainage problem in the manhole well. According to the requirements of the civil regulations, a sump must be set in the manhole, but I don’t know what method to use for centralized drainage.
3. The spacing of manhole wells is 150m according to the specification, while the atlas is 50m. I don't know which one shall prevail, but there are still other regulations.
4. Are there other atlases for reference? In addition to standard wells, can you design the shape and size of the well by yourself?
5. What matters should be paid attention to during the design and construction of this laying method.
Answer: 1. Non-standard wells can be designed according to needs;
2. For drainage in the well hole, if it is possible to install a drainage pump, a drainage pump should be installed. If there is no way to install a drainage pump, set up an overflow hole at the bottom of the sump. Don't seal it with concrete, let the water penetrate naturally. , But it depends on the local groundwater level;
3. I usually consider the spacing of manhole wells according to 50~70;
4. I personally think that it is not necessary for small municipal power distribution to build wells in accordance with the requirements of the atlas, just non-standard;
5. The concrete piping has not been done before, but please refer to GB50217-2007 P32 5.4.6 about the precautions and requirements for the use of piping.
Cable trench laying
Pay attention to the laying of cable trenches. Cables of different voltage levels must be installed in different brackets. Pay attention to drainage measures in the cable trench itself. And consider measures to prevent small animals such as rats from entering.
Question 1. How many cables need to be laid in a cable trench?
Answer: According to "Measures 2009 6.10 Section 8 or less, it is recommended to use direct burying, 8 to 12 cables are recommended to use pipes, 12 to 18 cables are recommended to use cable trenches, and 18 or more cables are recommended to use cable tunnels." These are all suggestions. It can be combined with actual engineering reference, and it is not so fixed. As for cable trenches and cable tunnels, it is not the difference between the number of cables, but the difference between maintenance and importance.
It mainly depends on factors such as engineering conditions, environmental characteristics and the number of cable types, as well as the selection of requirements that meet the requirements of reliable operation, easy maintenance and reasonable technology and economy. It is not sure whether there are mandatory index requirements. The specific plan can be determined by referring to the relevant content in section 5.2 of GB50217-2007 P28.
Question 2. How to calculate the current carrying capacity of the cable laid in the cable trench?
answer:
Netizen 1: (Considering the laying of the bridge, considering that the bridge is in the air and there is a cover in the cable trench, the derating factor is 0.96.)
Netizen 2: (The correlation coefficient of ampacity can refer to GB T16895.15-2002 "Electrical Installations of Buildings-Part 5, Section 523, Cabling System Ampacity". I personally think that it is more appropriate to consider the coefficient of the ladder frame.)
Question 3. Can the bus duct be laid along the cable trench?
Answer: There is no requirement. The depth of the cable trench is determined according to the number of your cables and the number of cable types. For example, there are control cables, low-voltage power cables, and high-voltage power cables. Generally, there are three layers, usually between each layer. The spacing is 250~300, so the height is determined.
Question 4. Does a cable well need to be built for directly buried cables?
Question supplement: For the first project, high-level hospitals, to save money, choose oil-immersed transformers to be installed outdoors, 15 meters away from the building (including a 6-meter road in the middle). The low-voltage power distribution room is located under the hospital. In order to save investment, I want to use The bus duct (carrying current 3000A) is laid along the cable trench to the underground power distribution room of the building. Is it feasible?
Answer: It should be possible to use intensive busbars that meet the requirements of the corresponding IP level. For example, Siemens has busbars that can be laid under water. However, the cost of using dense busbars will be relatively high. It is necessary to comprehensively consider which is better to choose dry transformer or busbar. Personally, it is recommended to use dry-type transformers and place them indoors. The maintenance workload will be smaller, and the failure rate will be lower.
Question 5. How many cables can be laid in the cable trench without brackets?
Answer: Generally, brackets are required. If there is no bracket, the maintenance of the cables in the cable trench will be more troublesome. If the project is not large and the number of cables is small, it does not matter if it is not installed, but the heat dissipation conditions will be worse, and if there is water in the trench, it will also affect the cables.
Question 6. Can high and low voltage cables be laid in a shared cable trench?
Question supplement: Outdoor cable trench, with a width of 1200mm, supports on both sides, with 10KV high-voltage cables on one side, and 1KV low-voltage cables and control cables on the other side. Does it comply with the specifications? What should I pay attention to?
Answer: It can be laid in a shared cable trench. For specific requirements, please refer to the requirements of GB 50217-2007 P24 5.1.3 and 5.1.4.
Question 7. What is the distance between the cable trench and the road?
Answer: This is mainly to consider the force of the cable trench cover. If there is no problem with the force, there is no problem. It is generally installed on the sidewalk or where the motor vehicle does not pass.
Question 8. Do I need to use armored cables when laying cables in cable trenches?
Supplement to the problem: technical measures say: when the cable is laid in a cable trench or a cable tunnel, it should be considered to choose a steel tape armored plastic outer sheath type cable with anti-termite and anti-rodent functions. But it seems that this point is not clearly stated in the specification! Can it be unarmored?
Answer: There is no mandatory requirement to use armor for direct buried cables, and there is no more cable trench. According to different environmental requirements, (if rat activities are rampant in this area, armor is recommended) generally there is no mandatory requirement.
Question 9. In the cable trench, when the strong current cable and the weak current cable are laid in layers on the same side support, what is the minimum distance?
Answer: Separate the weak current cables with a metal plate, and ground the metal plate at the same time! It is best to shim the iron plate (or metal slot box) on the uppermost support, the iron plate is grounded, and the weak current cable is placed on the iron plate (in the slot box).
According to GB 50217-2007 5.1.3 Article 1: Power cables with high to low voltage levels, control and signal cables from strong current to weak current, and communication cables should be arranged in the order of "from top to bottom". It can be determined according to GB50054-2011 table 7.6.23.


 Company Profiles
Company Profiles Company Culture
Company Culture Message
Message Honor
Honor Video Center
Video Center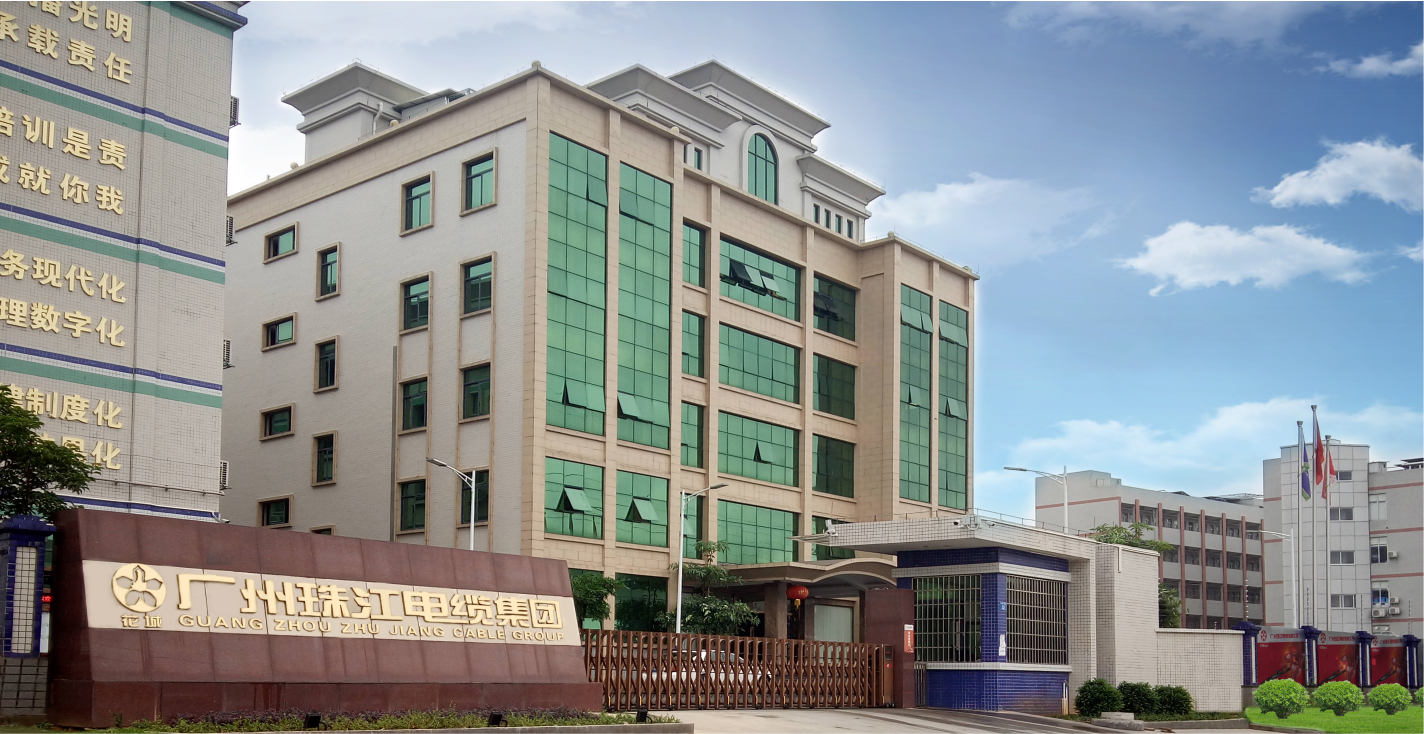 Company Reality
Company Reality Pearl River Cable
Pearl River Cable Low Voltage Cable
Low Voltage Cable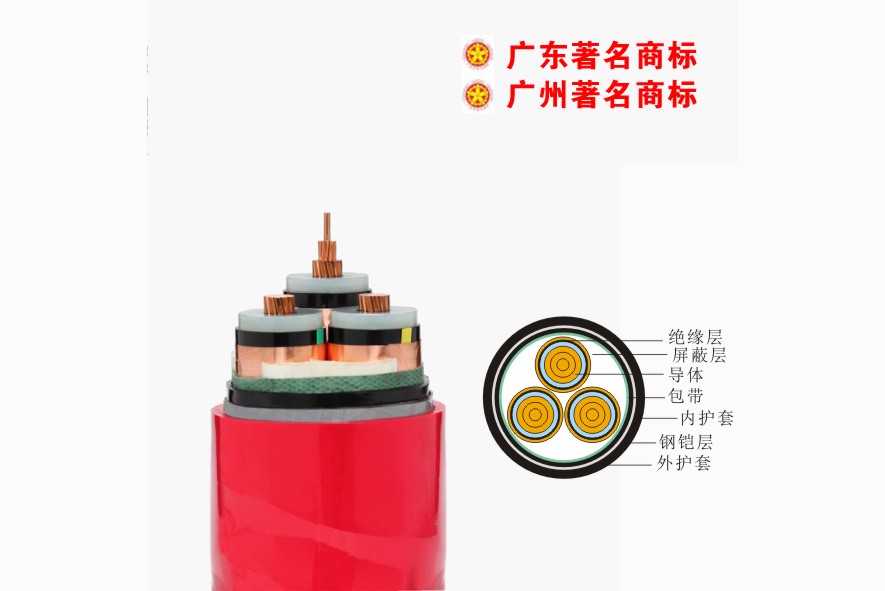 Medium Voltage
Medium Voltage Mineral Cable
Mineral Cable Control Signal Cable
Control Signal Cable Corporate News
Corporate News Cable Information
Cable Information Media Reports
Media Reports Network Reprint
Network Reprint