Types and performance analysis of nuclear-grade cables
Types and performance analysis of nuclear-grade cables
There are many types and quantities of nuclear-grade cables. According to estimates, a million-kilowatt nuclear power unit needs more than 100 types of cables, with a total length of nearly 2 million meters, and a value of about 100 million yuan. If divided by purpose, there are five categories: power cables, control cables, measurement cables, communication cables, and fire-resistant cables (silicon insulated cables). They should not only have the general characteristics of ordinary cables, but also have low-smoke, halogen-free, flame-retardant properties, and specific environmental resistance (such as radiation resistance, LOCA resistance). Although there are cable companies specializing in the development and production of nuclear-grade cables in China, there are still a few companies that can truly produce excellent nuclear-grade cables.
The special performance requirements of nuclear-grade cables make nuclear-grade cables compared with general industrial cables. The biggest difference lies in the performance requirements of cable materials for nuclear power plants. Low-smoke, halogen-free and flame-retardant. Ordinary low-voltage flame-retardant cables are generally made of PVC and other chlorine-containing cables. Polymer is used for insulation and sheath.
The insulation and sheath materials of nuclear-grade cables must be made of low-smoke, non-toxic, non-corrosive halogen-free flame-retardant cable materials, such as thermoplastic flame-retardant halogen-free or cross-linked flame-retardant halogen-free materials to meet special requirements. Nuclear safety requirements. In the event of a fire, a halogen-free cable emits a very low amount of smoke and is non-toxic and corrosive. Its flame-retardant components can effectively play a flame-retardant effect and will not make the cable a channel for flame propagation.
The halogen-free cable uses halogen-free polymer as the base material, which will not produce acid gas during combustion, so its toxicity and corrosiveness are much lower than ordinary PVC cables.
Flame-retardant mechanism of flame-retardant halogen-free flame-retardant cables
Add a large amount of fillers such as aluminum hydroxide or magnesium hydroxide to the halogen-free polymer. They release crystal water and absorb a lot of heat when the cable burns, thereby inhibiting the temperature rise of the polymer, delaying thermal decomposition, and reducing the burning speed. . In addition, the water vapor generated by dehydration and decomposition can dilute the combustible gas and produce a flame retardant effect. The flame retardancy of polymers is usually evaluated by the oxygen index method, which represents the minimum oxygen content required for the sample to burn in a mixture of oxygen and nitrogen. The larger the index, the lower the flammability and the greater the flame retardancy. it is good. Generally, the oxygen index (OI) is at least 28 to have non-combustible characteristics.
Fire resistance
When people require the cable line to continue to play a role in the event of a fire, and when the cable needs to be erected on the line in a high-risk area due to use, the cable must have fire resistance. In the event of a fire alarm, this fire-resistant cable can still continue to operate safely within a certain period of time, providing electrical energy for the rescue of personnel and equipment. The fire resistance performance of nuclear cables is different according to the requirements of use, divided into general fire resistance performance requirements and special fire resistance performance requirements. The special fire resistance performance requirements are: 1000%, 5min burning test under the impact condition of the cable. After the flame is extinguished, the impact is continued for 5min. At the same time, the cable is flushed with high pressure water at the specified pressure. The cable is required to be continuously energized during the entire test.
After the United States formulated the IEEE 383 cable standard in 1974, nuclear power plant cables caught fire and extended combustion accidents each year, prompting people to pay attention to the stringency of flame-retardant test standards. For the finished cable for nuclear island, it is halogen-free/low smoke/flame retardant, that is, the finished cable is required to pass the IEC332-3 bundled combustion test, the combustion smoke concentration meets the technical requirements of IEC1034-2, and the burning corrosive gas meets the IEC754-2 According to the requirements of the specified recommended values, the insulated wire core has passed the single vertical burning test specified by IPCEAS-19-81.
Environmental resistance
Nuclear-grade cable materials must have the environmental resistance required by the inherent working environment of nuclear power plants, that is, heat resistance, radiation resistance, and LOCA resistance.
Heat resistance
As nuclear-grade cables often work in high-temperature environments, they are required to have long-term heat resistance performance. It is necessary to select polymers that meet the requirements for heat resistance and allow the cables to have a service life of more than forty years.
Radiation resistance
To ease the environment, severe environmental nuclear-grade cables are exposed to a large amount of radiation, the insulation and sheath materials will become brittle, and the mechanical properties will deteriorate. Therefore, as insulation and sheath materials for cables in nuclear power plants, they must have excellent radiation resistance.
Various polymers have different resistance to radiation. People usually add anti-radiation agent to the polymer to improve its resistance to radiation. Regarding the L0CA resistance of cables, different nuclear power plants have different requirements.
In summary, in addition to the performance of ordinary cables, nuclear-grade cables must also have halogen-free, low-smoke, and flame-retardant characteristics, and meet the requirements for completing safety functions in the normal and accidental environment of the laying area. The necessary performance requirements, that is, must meet the requirements of earthquake resistance, normal and accident working conditions-radiation exposure, LOCA/HELB accident working environment resistance, working temperature and service life within the design life of the power station.
In addition, the original design index for nuclear-grade cables is more than 40 years, and the next-generation nuclear power plant requires 60 years. Therefore, whether the original design can meet the requirements of use still needs further experimental verification. How to extend the service life of cables has become an important research topic.
Low-smoke halogen-free flame-retardant nuclear cable is a special cable with high performance level and difficult manufacturing. Even if it is an imported product, many problems have been exposed during the application process, and some are even serious. How to deal with and solve these problems is unavoidable. Whether it is possible to consider using low-smoke and low-halogen flame-retardant materials to produce special cables for nuclear power plants is an idea that workers in the cable industry can explore. Doing so can reduce the difficulty of cable material formulation design, can make the production process easier to implement, the product quality will be more reliable, and it will be safer in practical applications.
Nuclear-grade cable is a cable variety with high performance and difficult manufacturing technology. At present, the production technology is not fully mature, and further research is needed.
Disclaimer: The information comes from the Internet, periodicals, or provided by the author. The content does not represent the views of this website and is for reference only. If there is an infringement of your copyright or other behavior that harms your interests, we will immediately correct it and delete the relevant content.


 Company Profiles
Company Profiles Company Culture
Company Culture Message
Message Honor
Honor Video Center
Video Center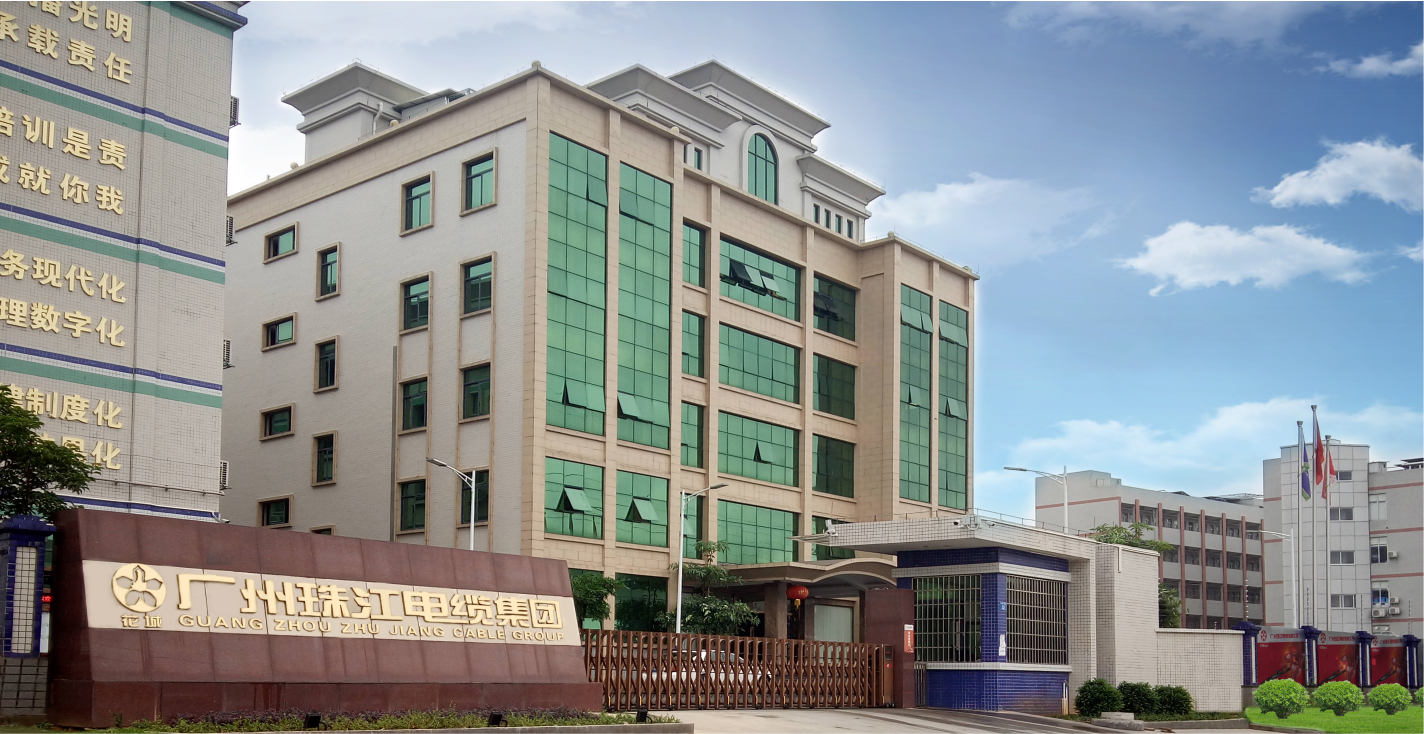 Company Reality
Company Reality Pearl River Cable
Pearl River Cable Low Voltage Cable
Low Voltage Cable Medium Voltage
Medium Voltage Mineral Cable
Mineral Cable Control Signal Cable
Control Signal Cable Corporate News
Corporate News Cable Information
Cable Information Media Reports
Media Reports Network Reprint
Network Reprint