What are the characteristics of mineral cables BTTZ and YTTW!
Guangzhou Pearl River Cable Co., Ltd.
At present, there are two types of fireproof cables in the domestic market. One is the traditional mineral insulated cable (model BTTZ) that uses magnesium oxide as insulation, and the other is the inorganic mineral insulated cable (model For YTTW).
The copper conductive core, copper outer sheath and insulation layer of the traditional mineral insulated cable (BTTZ) are densely integrated. Production and use abroad have a history of nearly 80 years, and domestic production and use have a history of more than 20 years. And some major projects at home and abroad have been widely used and the effect is very good.
Inorganic mineral insulated cables are also called flexible fire-resistant cables (YTTW). The conductor is made up of multiple strands of copper wire. Multi-layer mica tape is used as the insulating layer. The mica tape uses glass fiber cloth as the base material. The outer layer is longitudinally wrapped with copper tape and continuously welded to form a sheath, and then the smooth sheath is pressed into a spiral shape.
This article is mainly based on the test standards for cable testing at home and abroad, through the test methods (mainly some tests such as fire resistance), and the analysis of the test results to determine the performance of the two cables.
1. Fire resistance comparison test
The fire resistance test reflects the continuous power supply capability of the cable under fire conditions. In order to test the fire resistance of mineral insulated cables (BTTZ) and inorganic mineral insulated cables (YTTW), according to the fire resistance test regulations of GB/T19216 IEC331 BS6387, a comparison test was carried out on two cables with a specification of 4×25. The results are as follows:
GB/T19216 burned at 750℃ for 90min. Both cable samples passed the test
IEC331 burns at 750℃ for 90min. Both cable samples pass the test
BS6387 burned at 950℃ for 3h, both cable samples passed the test
Burning at 650℃ and spraying for 15min. Both cable samples passed the test
Burning at 950°C impacts once every 5 minutes for 15 minutes. Both cable samples passed the test
Observed from the samples in the test and the final test results show that the inorganic mineral insulated cable (i.e., flexible fire-resistant cable) under the condition of continuous high-temperature combustion, the mica, which plays the role of insulation and fire resistance, will fall off in powder form, and the glass cloth will become hard and brittle. However, due to the characteristics of the YTTW cable structure, there is a considerable gap between the sheath and the insulating layer, which provides space for the falling mica powder, so that it is very easy to cause a short circuit under the impact of external force.
The insulation layer of this cable is not a dense magnesium oxide layer like BTTZ cable, so its explosion-proof performance is not good. Combustible gas, gasoline, steam, etc. will spread to the cable connection through the gap between the cable sheath and the insulation layer. Electrical equipment or other areas with explosion-proof requirements, so in some important places, such as fire-fighting systems, if you choose WTTY cable, it is not a suitable choice from the point of view of fire-resistant (fire-resistant) performance alone.
2. Withstand voltage comparison test
The YTTW cable is boosted at a speed of 150V/s. Each time it lasts for 15 minutes, it fails to reach 2500V and is broken down at 1300V. After 3h, the voltage was applied again, and it was broken down at 20V. The cable cannot recover its performance after breakdown.
The BTTZ cable was boosted at a speed of 150V/s for 15 minutes each time, and no breakdown occurred to 2500V. The cable was broken down when the voltage continued to rise to 3500V. After 3 hours, the voltage was applied again, and the voltage was boosted at a speed of 150V/s for 15 minutes each time, and no breakdown occurred to 2500V. The breakdown of the cable can also restore its performance.
Through the experiment, it can be seen that the limit voltage of BTTZ cable is almost twice the voltage of YTTW. If an overvoltage is accidentally generated during the use of the cable, the cable will be broken down.
The insulation layer of the BTTZ cable is damaged due to the air ionization at the breakdown, causing the magnesium oxide to melt locally, but its composition will not change after it melts. After a period of time, it will still be dense magnesium oxide after solidification and crystallization, so the cable is still The original electrical performance can be restored. Once the YTTW cable is broken down, it can no longer restore its electrical performance and can only be scrapped.
3. Contrast test of current-carrying capacity
Test samples of YTTW and BTTZ cables with the same cross-section (4×25)
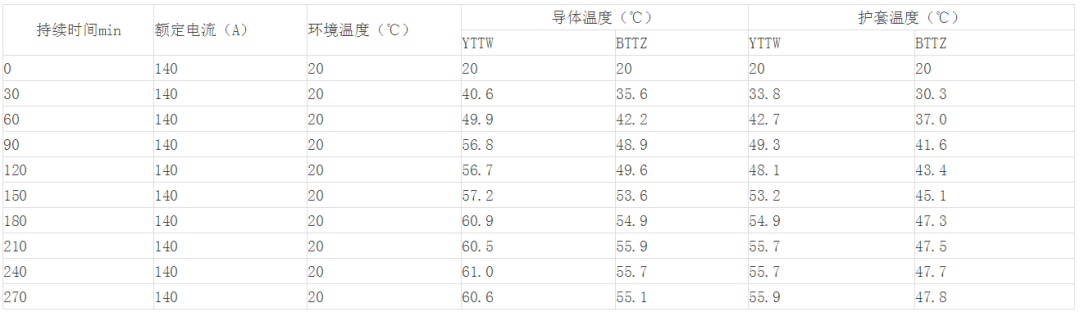
It can be seen from the test results that the conductor temperature and sheath temperature of the BTTZ cable are about 6°C lower than that of the WTTY cable under the same conditions. As for the cable itself, the type of insulation material and its heat resistance and heat dissipation performance can greatly affect the current carrying capacity of the cable.
Obviously, the heat dissipation performance of mica tape is worse than that of magnesium oxide. According to GB/T 16895, bare mineral insulated cables that do not allow people to contact flammable materials, the temperature of the metal sheath is 105℃, the ambient temperature is 30℃, and the current carrying capacity of the cable is 140A. .
The above test was actually carried out when the ambient temperature was 20. If the ambient temperature reaches 30°C, the surface temperature of the cable sheath will be higher. If the two cables are at the same ambient temperature, the surface temperature of the sheath will reach a certain value. The current carrying capacity of BTTZ cable will definitely be much larger than that of WTTY.
4. Other characteristics comparison
YTTW cables are also called flexible fireproof cables. First of all, BTTZ and YTTW cables are fixed cables and do not need to be moved as often as some organic cables. So flexibility is not an essential feature for this kind of cable.
And because of the structure and size of the cable, the allowable bending radius of YTTW cable during installation is obviously much larger than that of BTTZ cable. From this point of view, whether it is laid on a bridge or along a wall, it is not only unsightly but also prone to waste of space.
The outer diameter of the YTTW cable is larger than that of the BTTZ of the same cross-section, which will cause a lot of trouble for installation and construction when the installation space is limited.


 Company Profiles
Company Profiles Company Culture
Company Culture Message
Message Honor
Honor Video Center
Video Center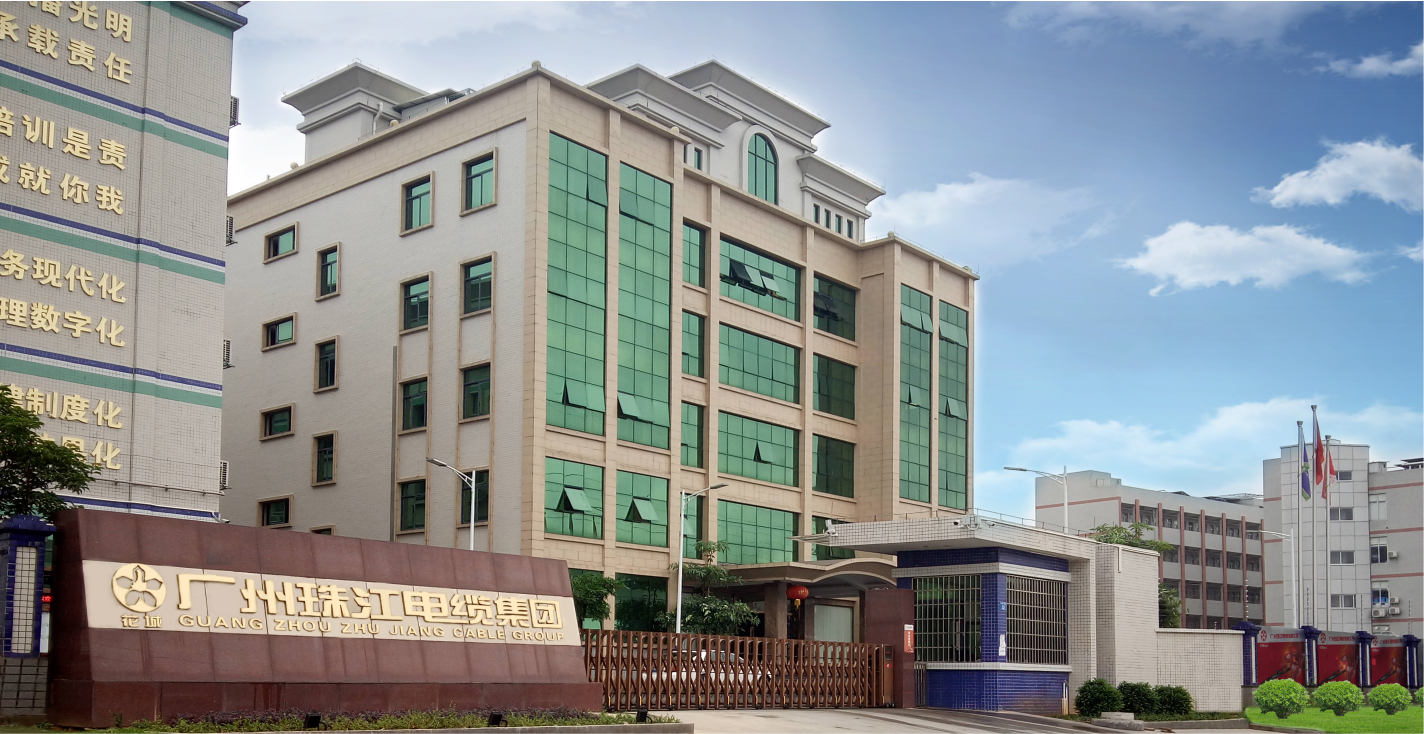 Company Reality
Company Reality Pearl River Cable
Pearl River Cable Low Voltage Cable
Low Voltage Cable Medium Voltage
Medium Voltage Mineral Cable
Mineral Cable Control Signal Cable
Control Signal Cable Corporate News
Corporate News Cable Information
Cable Information Media Reports
Media Reports Network Reprint
Network Reprint