Safe operation and maintenance of wires and cables
Safe operation and maintenance of wires and cables
(1) Corrosion monitoring
Use special instruments to measure the surrounding soil of adjacent lines. If it belongs to the anode area, corresponding measures should be taken to prevent the electrolytic corrosion of the metal sheath of the wire and cable. In the surrounding wet soil or soil filled with domestic waste, the metal sleeve often undergoes chemical corrosion and microbial corrosion. According to the measured voltage value of the anode area, select appropriate cathodic protection measures or drainage devices.
(2) Insulation supervision
Prepare a preventive test plan for each cable and wire according to its importance, find the weak links in it in time, and eliminate the defects that may cause accidents. Generally, after the preventive test, another DC voltage test is required for the outer protective layer to find and eliminate defects in the outer protective layer in time.
(3) Load monitoring
Generally, the maximum current value is specified according to the cross-sectional area of the conductor and the insulation type, and various instruments are used to measure the load current of the line or the temperature of the electrical sheath as the main load monitoring measure to prevent the insulation from exceeding the maximum allowable temperature and shortening the cable life.
(4) Temperature monitoring
Temperature measurement should be carried out in summer or at maximum load. When measuring the temperature of directly buried wires and cables, the soil temperature in the same section without other heat sources should be measured.



 Company Profiles
Company Profiles Company Culture
Company Culture Message
Message Honor
Honor Video Center
Video Center Company Reality
Company Reality Pearl River Cable
Pearl River Cable Low Voltage Cable
Low Voltage Cable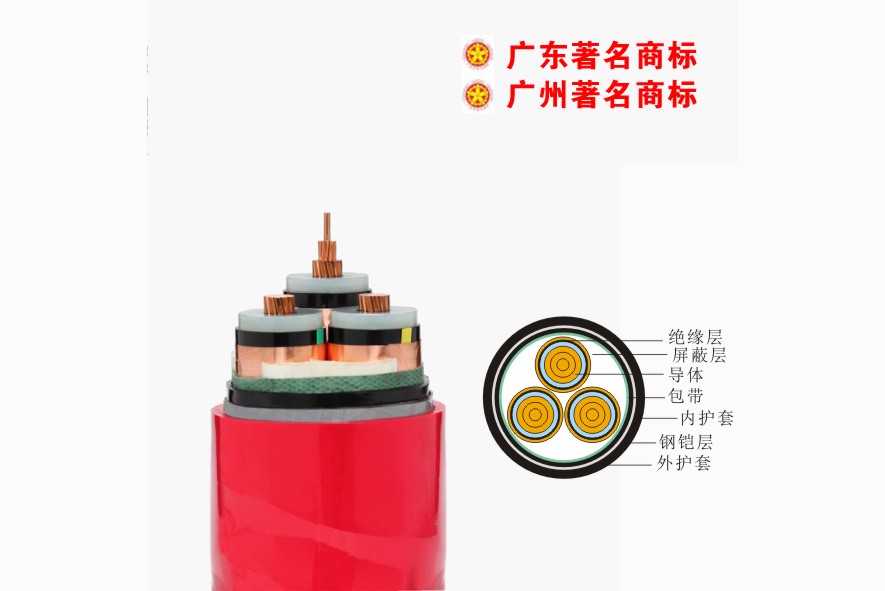 Medium Voltage
Medium Voltage Mineral Cable
Mineral Cable Control Signal Cable
Control Signal Cable Corporate News
Corporate News Cable Information
Cable Information Media Reports
Media Reports Network Reprint
Network Reprint